[<ReactComponent>]
Feliz offers a simple way to define React components using the [<ReactComponent>] attribute. This attribute can be applied to a function that returns a React element.
With the help of [<ReactComponent>] Feliz can ensure that the components are correctly transformend and called after transpilation to JavaScript.
If you are interested in what happens under the hood, here is a short summary of notable points:
Click to expand
-
Transform all arguments into an JavaScript object.
Tupled/curried arguments are transformed into object and exactly one argument as anonymous record type will be used as object.
Example: Tupled arguments
- F#
- jsx
module Example.ReactComponentTransform.Tupled
open Feliz
open Feliz.JSX
[<ReactComponent>]
let Component(text: string, count: int) =
Html.div [
Html.text text
Html.text count
]
import React from "react";
export function Component($props) {
const count = $props.count;
const text = $props.text;
return <div>
{text}
{count}
</div>;
}Example: Curried arguments
- F#
- jsx
module Example.ReactComponentTransform.Curried
open Feliz
open Feliz.JSX
[<ReactComponent>]
let Component (text: string) (count: int) =
Html.div [
Html.text text
Html.text count
]
import React from "react";
export function Component($props) {
const count = $props.count;
const text = $props.text;
return <div>
{text}
{count}
</div>;
}Example: Anonymous Record Type
- F#
- jsx
module Example.ReactComponentTransform.AnonymRecordType
open Feliz
open Feliz.JSX
type Props = {|
text: string
count: int
|}
[<ReactComponent>]
let Component (anoRecordType: Props) =
Html.div [
Html.text anoRecordType.text
Html.text anoRecordType.count
]
import React from "react";
export function Component(anoRecordType) {
return <div>
{anoRecordType.text}
{anoRecordType.count}
</div>;
}Example: Record Type ⚠️
warningRecord types are not transformed and passed as is. Record Types are transpiled by Fable into a class like structure so we loose equality and possibly attached functions if we deconstruct them into a js object.
- F#
- jsx
module Example.ReactComponentTransform.RecordType
type Props = {
text: string
count: int
}
open Feliz
open Feliz.JSX
[<ReactComponent>]
let Component (recordType: Props) =
Html.div [
Html.text recordType.text
Html.text recordType.count
]
import { Record } from "../../../fable_modules/fable-library-js.5.0.0-alpha.20/Types.js";
import { record_type, int32_type, string_type } from "../../../fable_modules/fable-library-js.5.0.0-alpha.20/Reflection.js";
import React from "react";
export class Props extends Record {
constructor(text, count) {
super();
this.text = text;
this.count = (count | 0);
}
}
export function Props_$reflection() {
return record_type("Example.ReactComponentTransform.RecordType.Props", [], Props, () => [["text", string_type], ["count", int32_type]]);
}
export function Component($props) {
const recordType = $props.recordType;
return <div>
{recordType.text}
{recordType.count}
</div>;
} -
Component will be called using the
createElementfunction from React. -
Import
Reactautomatically.
export default
You can pass a boolean parameter to the attribute to export the component as the default export of the module.
[<ReactComponent(exportDefault = true)>]
let Component() = ...
// or
[<ReactComponent(true)>]
let Component() = ...
import .. from
You can pass string arguments to the attribute to import specific named imports from a file.
For file imports use relative paths only! They MUST start with ./ or ../! Otherwise Fable might not be able to resolve the path correctly
[<ReactComponent(import = "Counter", from = "../Counter")>] // from file
let Component() = React.Imported()
[<ReactComponent(import = "Counter", from = "my-awesome-counter")>] // from node_modules
let Component() = React.Imported()
Counter: 42
Counter: 10
Show code
- NativeCounter.tsx
- ReactComponentImport.fs
import React from "react";
interface Props {
init?: number;
}
export function Counter({init = 42}: Props) {
const [count, setCount] = React.useState(init);
return (
<div>
<h1>Counter: {count}</h1>
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>Increment</button>
<button onClick={() => setCount(count - 1)}>Decrement</button>
</div>
);
}
module Examples.Feliz.ReactComponentImport
open Feliz
type Component =
[<ReactComponent("Counter", "./NativeCounter")>]
static member Counter(?init: int) = React.Imported()
[<ReactComponent(true)>]
static member Example() =
Html.div [
Component.Counter()
Component.Counter(10)
]
[<ReactMemoComponent>]
React memo components can be created using the [<ReactMemoComponent>] attribute. It works the same way as [<ReactComponent>], but wraps the component in React.memo and ensures that it is defined as a const in the generated JavaScript code.
Check the output in the browser console
The child component below is memoized using the [<ReactMemoComponent>] attribute. It only rerenders when its props change.
Show code
module Example.MemoAttribute
open Feliz
open Browser.Dom
[<ReactMemoComponent>]
let RenderTextWithEffect (text: string) =
React.useEffect (fun () -> console.log("Rerender!", text) )
Html.div [
prop.text text;
prop.testId "memo-attribute"
]
[<ReactComponent(true)>]
let Main () =
let isDark, setIsDark = React.useState(false)
let text, setText = React.useState("Hello, world!")
let fgColor = if isDark then color.white else color.black
let bgColor = if isDark then color.black else color.white
Html.div [
prop.style [style.border(1, borderStyle.solid, fgColor); style.padding 20; style.color fgColor; style.backgroundColor bgColor]
prop.children [
Html.h3 "Check the output in the browser console"
Html.p "The child component below is memoized using the [<ReactMemoComponent>] attribute. It only rerenders when its props change."
Html.button [
prop.text "Toggle Dark Mode"
prop.onClick (fun _ -> setIsDark(not isDark))
]
Html.input [
prop.value text
prop.onChange setText
]
RenderTextWithEffect(text)
]
]
areEqual - Feliz predefined functions
Feliz features prewritten equality functions for common scenarios that can be used with the areEqualFn parameter of the [<ReactMemoComponent>] attribute. This parameter
accepts an integer value that corresponds to the desired equality function:
0/AreEqualFn.FsEquals- Uses F#'s built-in equality comparison (=) for all props. So everything that normally returns true when using F# equality=will return true here as well.1/AreEqualFn.FsEqualsButFunctions- Uses F#'s built-in equality comparison (=) for all props, but ignores all functions in props. This is useful when you have functions as props that are recreated on each render, but you want to ignore them for equality checks.
You can also use defined integer constants for example: AreEqualFn.FsEquals for better readability.
Show code
module Examples.Feliz.ReactMemoComponentAreEqualFn
open Feliz
// Memo using F# equality but ignoring function properties
[<ReactMemoComponent(AreEqualFn.FsEqualsButFunctions)>]
let MemoFsEqualsButFunctions (values: int list, fn: int -> int) =
let renderCount = React.useRef 0
renderCount.current <- renderCount.current + 1
Html.div [
prop.testId "memo-fs-bf-count";
prop.text (string renderCount.current)
]
// This will rerender when parent renders due to function property change
[<ReactMemoComponent(AreEqualFn.FsEquals)>]
let MemoFsEquals (values: int list, fn: int -> int) =
let renderCount = React.useRef 0
renderCount.current <- renderCount.current + 1
Html.div [
prop.testId "memo2-fs-bf-count";
prop.text (string renderCount.current)
]
// This will alway rerender when parent renders
[<ReactComponent>]
let ComparisonComponent (values: int list, fn: int -> int) =
let renderCount = React.useRef 0
renderCount.current <- renderCount.current + 1
Html.div [
prop.testId "fs-bf-count";
prop.text (string renderCount.current)
]
[<ReactComponent(true)>]
let ParentWithFnFsButFunctions() =
let state, setState = React.useState 0
let fn = fun x -> x + state // New function instance on each render
let values = [ 1; 2 ] // New list instance on each render
Html.div [
Html.button [
prop.testId "btn-fn-bf";
prop.onClick (fun _ -> setState(state + 1));
prop.text "Trigger Rerender by changing state of parent!"
]
MemoFsEqualsButFunctions (values, fn)
MemoFsEquals (values, fn)
ComparisonComponent (values, fn)
]
areEqual - JavaScript code emit
You can pass a custom equality function to the [<ReactMemoComponent>] attribute using the areEqual parameter. The value must be a JavaScript function expressed as a string. This function will be used to determine whether the component should re-render based on its props.
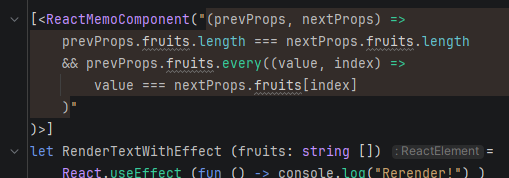
[<ReactMemoComponent("(prevProps, nextProps) =>
prevProps.fruits.length === nextProps.fruits.length
&& prevProps.fruits.every((value, index) =>
value === nextProps.fruits[index]
)"
)>]
let RenderTextWithEffect (fruits: string []) =
This behavior is similiar to the [<Emit>] attribute in Fable.
areEqual is implemented using the [<StringSyntax("javascript")>] attribute. This will provide syntax highlighting and basic validation in supported editors.
Example: Rider
 ;
;
The areEqual functions runs on the transformed js output, so you must assume, that your params are passed as a single object containing all props!
Check the output in the browser console
The child component below is memoized using the [<ReactMemoComponent>] attribute. It only rerenders when the areEqual function returns false.
Show code
module Example.MemoAttributeAreEqualEmit
open Feliz
open Browser.Dom
[<ReactMemoComponent("(prevProps, nextProps) =>
prevProps.fruits.length === nextProps.fruits.length
&& prevProps.fruits.every((value, index) =>
value === nextProps.fruits[index]
)"
)>]
let RenderTextWithEffect (fruits: string []) =
React.useEffect (fun () -> console.log("Rerender!") )
Html.div [
prop.text (fruits |> String.concat ", ");
prop.testId "memo-attribute"
]
[<ReactComponent(true)>]
let Main () =
let isDark, setIsDark = React.useState(false)
let input, setInput = React.useState("")
// This will stay the same array if it does not change
let fruits, setFruits = React.useState([|"apple"; "orange"; "banana"|])
// This creates a new array reference on every render, triggering a rerender of the child component, without custom equality check
let sortedFruits =
fruits
|> Array.sort
let isValidInput = System.String.IsNullOrEmpty input |> not && fruits |> Array.contains input |> not
let fgColor = if isDark then color.white else color.black
let bgColor = if isDark then color.black else color.white
Html.div [
prop.style [style.border(1, borderStyle.solid, fgColor); style.padding 20; style.color fgColor; style.backgroundColor bgColor]
prop.children [
Html.h3 "Check the output in the browser console"
Html.p "The child component below is memoized using the [<ReactMemoComponent>] attribute. It only rerenders when the areEqual function returns false."
Html.button [
prop.text "Toggle Dark Mode"
prop.onClick (fun _ -> setIsDark(not isDark))
]
Html.input [
prop.value input
prop.onChange setInput
]
Html.button [
prop.text "Change Fruits Array"
prop.disabled (not isValidInput)
prop.onClick (fun _ ->
if isValidInput then
[|yield! fruits; input|] |> setFruits
setInput ""
)
]
RenderTextWithEffect(sortedFruits)
]
]
areEqual - F# function call emit
We can also emit a call to a f# function defined in the same file. This function must have the correct signature to be used as an equality function.
let areEqualFn prop1 prop2 =
prop1 = prop2
[<ReactMemoComponent(nameof areEqualFn)>] // or "areEqualFn"
let RenderTextWithEffect (fruits: string []) =
React.useEffect (fun () -> console.log("Rerender!") )
Html.div [
prop.text (fruits |> String.concat ", ");
prop.testId "memo-attribute"
]
This works as f# equality does not check reference equality for arrays and sequences, but checks the content of them. Which is what is used by shallow comparison of React.memo.
The areEqual functions runs on the transformed js output, so you must assume, that your params are passed as a single object containing all props!
In the example above, if you want to compare the fruits prop, you need to access it as prop1.fruits and prop2.fruits in the areEqualFn function:
let areEqualFn (prop1: {|fruits: string []|}) (prop2: {|fruits: string []|}) =
prop1.fruits = prop2.fruits
If you define your equality function as static member or inside a module, Fable might mangle the name of the function during transpilation. In this case, you need to provide the mangled name to the areEqual parameter. You can see this behavior int his Fable Repl.
module EqualityFn =
let areEqualFn prop1 prop2 =
prop1 = prop2
Check the output in the browser console
The child component below is memoized using the [<ReactMemoComponent>] attribute. It only rerenders when the areEqual function returns false.
Show code
- MemoAttributeAreEqualEmitFnName.fs
- MemoAttributeAreEqualEmitFnName.jsx
module Example.MemoAttributeAreEqualEmitFnName
open Feliz
open Browser.Dom
let areEqualFn prop1 prop2 =
prop1 = prop2
[<ReactMemoComponent(nameof areEqualFn)>] // or "areEqualFn"
let RenderTextWithEffect (fruits: string []) =
React.useEffect (fun () -> console.log("Rerender!") )
Html.div [
prop.text (fruits |> String.concat ", ");
prop.testId "memo-attribute"
]
[<ReactComponent(true)>]
let Main () =
let isDark, setIsDark = React.useState(false)
let input, setInput = React.useState("")
// This will stay the same array if it does not change
let fruits, setFruits = React.useState([|"apple"; "orange"; "banana"|])
// This creates a new array reference on every render, triggering a rerender of the child component, without custom equality check
let sortedFruits =
fruits
|> Array.sort
let isValidInput = System.String.IsNullOrEmpty input |> not && fruits |> Array.contains input |> not
let fgColor = if isDark then color.white else color.black
let bgColor = if isDark then color.black else color.white
Html.div [
prop.style [style.border(1, borderStyle.solid, fgColor); style.padding 20; style.color fgColor; style.backgroundColor bgColor]
prop.children [
Html.h3 "Check the output in the browser console"
Html.p "The child component below is memoized using the [<ReactMemoComponent>] attribute. It only rerenders when the areEqual function returns false."
Html.button [
prop.text "Toggle Dark Mode"
prop.onClick (fun _ -> setIsDark(not isDark))
]
Html.input [
prop.value input
prop.onChange setInput
]
Html.button [
prop.text "Change Fruits Array"
prop.disabled (not isValidInput)
prop.onClick (fun _ ->
if isValidInput then
[|yield! fruits; input|] |> setFruits
setInput ""
)
]
RenderTextWithEffect(sortedFruits)
]
]
import { stringHash, comparePrimitives, equals } from "../../fable_modules/fable-library-js.5.0.0-alpha.20/Util.js";
import { createElement, useState, useEffect, memo } from "react";
import React from "react";
import { some } from "../../fable_modules/fable-library-js.5.0.0-alpha.20/Option.js";
import { HtmlHelper_createElement } from "../../src/Feliz/Html.jsx";
import { isNullOrEmpty, join } from "../../fable_modules/fable-library-js.5.0.0-alpha.20/String.js";
import { ofArray, singleton } from "../../fable_modules/fable-library-js.5.0.0-alpha.20/List.js";
import { contains, sort } from "../../fable_modules/fable-library-js.5.0.0-alpha.20/Array.js";
import { defaultOf } from "../../fable_modules/fable-library-js.5.0.0-alpha.20/Util.js";
import { singleton as singleton_1, append, delay, toArray } from "../../fable_modules/fable-library-js.5.0.0-alpha.20/Seq.js";
export function areEqualFn(prop1, prop2) {
return equals(prop1, prop2);
}
export const RenderTextWithEffect = (memo)(function RenderTextWithEffect(props) { return (($props) => {
const fruits = $props.fruits;
useEffect(() => {
console.log(some("Rerender!"));
});
return HtmlHelper_createElement("div", ofArray([["children", singleton(join(", ", fruits))], ["data-testid", "memo-attribute"]]));
})(props); }, areEqualFn);
export function Main() {
let value_9;
const patternInput = useState(false);
const isDark = patternInput[0];
const patternInput_1 = useState("");
const setInput = patternInput_1[1];
const input = patternInput_1[0];
const patternInput_2 = useState(["apple", "orange", "banana"]);
const fruits = patternInput_2[0];
const sortedFruits = sort(fruits, {
Compare: (x, y) => (comparePrimitives(x, y) | 0),
});
const isValidInput = !isNullOrEmpty(input) && !contains(input, fruits, {
Equals: (x_1, y_1) => (x_1 === y_1),
GetHashCode: (x_1) => (stringHash(x_1) | 0),
});
const fgColor = isDark ? "#FFFFFF" : "#000000";
return HtmlHelper_createElement("div", ofArray([["style", {
border: (((1 + "px ") + "solid") + " ") + fgColor,
padding: 20,
color: fgColor,
backgroundColor: isDark ? "#000000" : "#FFFFFF",
}], ["children", [createElement("h3", defaultOf(), "Check the output in the browser console"), (value_9 = "The child component below is memoized using the [<ReactMemoComponent>] attribute. It only rerenders when the areEqual function returns false.", createElement("p", defaultOf(), value_9)), HtmlHelper_createElement("button", ofArray([["children", singleton("Toggle Dark Mode")], ["onClick", (_arg) => {
patternInput[1](!isDark);
}]])), HtmlHelper_createElement("input", ofArray([["value", input], ["onChange", (ev) => {
setInput(ev.target.value);
}]])), HtmlHelper_createElement("button", ofArray([["children", singleton("Change Fruits Array")], ["disabled", !isValidInput], ["onClick", (_arg_1) => {
if (isValidInput) {
patternInput_2[1](toArray(delay(() => append(fruits, delay(() => singleton_1(input))))));
setInput("");
}
}]])), createElement(RenderTextWithEffect, {
fruits: sortedFruits,
})]]]));
}
export default Main;
[<ReactLazyComponent>]
React lazy components can be created using the [<ReactLazyComponent>] attribute. It works similarly to [<ReactComponent>], but is intended for components that are loaded dynamically using React.lazy.
There are two ways to define a lazy component with [<ReactLazyComponent>]:
Remember that only default exports can be lazy loaded!
[<ReactComponent(true)>] // like this!
From existing component
This approach allows to wrap an existing component in a lazy-loaded component.
If you have optional parameters, you will need to add the arguments you want to use to the wrapper. Otherwise the F# compiler will assume a None for all. (See examples below!)
- F#
- JSX
- F# List Component
module Examples.Feliz.ReactLazyComponent
open Feliz
[<ReactLazyComponent>]
let private LazyLists(list: int list option) = Examples.Feliz.RenderingLists.RenderingLists.Example(?list = list)
[<ReactLazyComponent>]
let private LazyListsNoArg = Examples.Feliz.RenderingLists.RenderingLists.Example
[<Fable.Core.Erase; Fable.Core.Mangle(false)>]
type Examples =
[<ReactLazyComponent>]
static member LazyList(?list: int list) = Examples.Feliz.RenderingLists.RenderingLists.Example(?list = list)
[<ReactComponent(true)>]
static member Main() =
Html.div [
Html.h1 "ReactLazyComponent Example"
Html.h2 "With argument"
LazyLists(Some [1;2;3;4;5])
Html.h2 "Without argument"
LazyListsNoArg()
Html.h2 "Using static member"
Examples.LazyList([10;20;30])
]
import { createElement, lazy } from "react";
import React from "react";
import { defaultOf } from "../../fable_modules/fable-library-js.5.0.0-alpha.20/Util.js";
import { ofArray } from "../../fable_modules/fable-library-js.5.0.0-alpha.20/List.js";
export const LazyLists = lazy(() => {
return import("./RenderingLists.jsx");
});
export const LazyListsNoArg = lazy(() => {
return import("./RenderingLists.jsx");
});
export const LazyList = lazy(() => {
return import("./RenderingLists.jsx");
});
export function Main() {
const children_8 = ofArray([createElement("h1", defaultOf(), "ReactLazyComponent Example"), createElement("h2", defaultOf(), "With argument"), createElement(LazyLists, {
list: ofArray([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]),
}), createElement("h2", defaultOf(), "Without argument"), createElement(LazyListsNoArg, null), createElement("h2", defaultOf(), "Using static member"), createElement(LazyList, {
list: ofArray([10, 20, 30]),
})]);
return createElement("div", defaultOf(), ...children_8);
}
export default Main;
module Examples.Feliz.RenderingLists
open Feliz
type RenderingLists =
[<ReactComponent(true)>]
static member Example(?list: int list) =
let items = defaultArg list [ 0 .. 5 ] //any list/seq/array
Html.div [
Html.h2 "List rendering using for loop"
Html.ul [
Html.li "Static item 1"
for item in items do // f# for loop, nicely combinable with other children
Html.li [
prop.key item
prop.text (sprintf "Item %i" item)
]
]
Html.h2 "List rendering using List.map"
items // f# pipe style
|> List.map (fun item ->
Html.li [
prop.key item
prop.text (sprintf "Item %i" item)
])
|> Html.ol
]
From path
Alternatively you can specify a path to a module that contains a default export of a React component.
This approach will not have type safety for the component props! It is similiar to writing a JavaScript binding!
- F#
- JSX
- F# List Component
module Examples.Feliz.ReactLazyComponentPath
open Feliz
[<ReactLazyComponent>]
let private LazyLists(list: int list option) = React.DynamicImported "./RenderingLists"
[<ReactLazyComponent>]
let private LazyListsNoArg() = React.DynamicImported "./RenderingLists"
[<Fable.Core.Erase; Fable.Core.Mangle(false)>]
type Examples =
[<ReactLazyComponent>]
static member LazyList(?list: int list) = React.DynamicImported "./RenderingLists"
[<ReactComponent(true)>]
static member Main() =
Html.div [
Html.h1 "ReactLazyComponent Example"
Html.h2 "With argument"
LazyLists(Some [1;2;3;4;5])
Html.h2 "Without argument"
LazyListsNoArg()
Html.h2 "Using static member"
Examples.LazyList([10;20;30])
]
import { createElement, lazy } from "react";
import React from "react";
import { defaultOf } from "../../fable_modules/fable-library-js.5.0.0-alpha.20/Util.js";
import { ofArray } from "../../fable_modules/fable-library-js.5.0.0-alpha.20/List.js";
export const LazyLists = lazy(() => {
return import("./RenderingLists");
});
export const LazyListsNoArg = lazy(() => {
return import("./RenderingLists");
});
export const LazyList = lazy(() => {
return import("./RenderingLists");
});
export function Main() {
const children_8 = ofArray([createElement("h1", defaultOf(), "ReactLazyComponent Example"), createElement("h2", defaultOf(), "With argument"), createElement(LazyLists, {
list: ofArray([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]),
}), createElement("h2", defaultOf(), "Without argument"), createElement(LazyListsNoArg, null), createElement("h2", defaultOf(), "Using static member"), createElement(LazyList, {
list: ofArray([10, 20, 30]),
})]);
return createElement("div", defaultOf(), ...children_8);
}
export default Main;
module Examples.Feliz.RenderingLists
open Feliz
type RenderingLists =
[<ReactComponent(true)>]
static member Example(?list: int list) =
let items = defaultArg list [ 0 .. 5 ] //any list/seq/array
Html.div [
Html.h2 "List rendering using for loop"
Html.ul [
Html.li "Static item 1"
for item in items do // f# for loop, nicely combinable with other children
Html.li [
prop.key item
prop.text (sprintf "Item %i" item)
]
]
Html.h2 "List rendering using List.map"
items // f# pipe style
|> List.map (fun item ->
Html.li [
prop.key item
prop.text (sprintf "Item %i" item)
])
|> Html.ol
]